Medical Need
The evolution on the silent pandemic
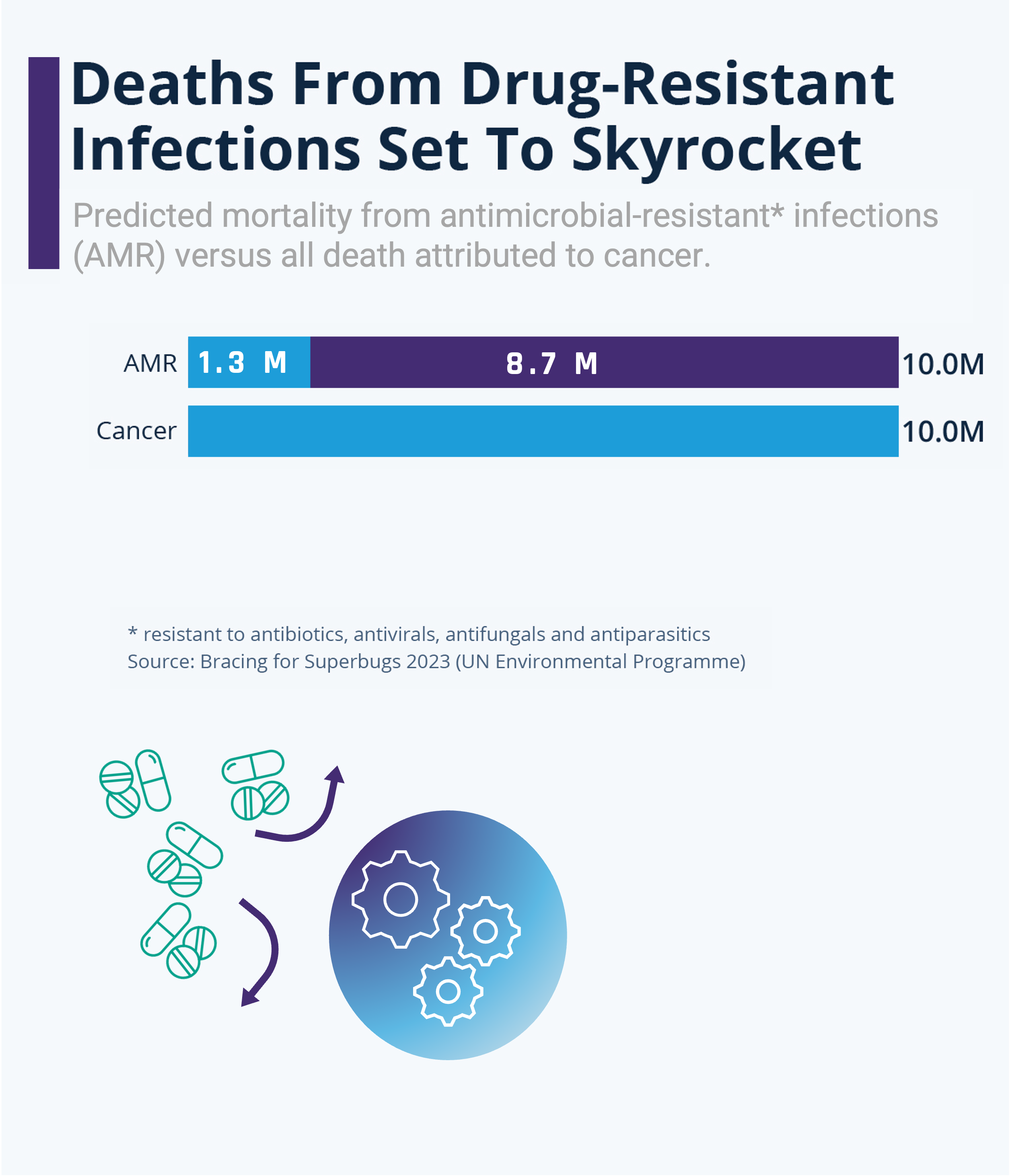
Infectious diseases remain the leading cause of death worldwide, mainly because of anti-infective resistance. Antimicrobial resistance, resulting from their misuse in humans and animals, has become a serious threat to the effective treatment of an ever-increasing number of infections. Resistant pathogens cause 1,3 millions deaths a year, and WHO projections indicate that 10 million deaths a year are expected by 2050.
The battle against infectious diseases must be fought on several fronts: the development of new classes of anti-infective molecules, the implementation of solutions to reduce the number of nosocomial infections, and the invention of preventive solutions.
Polypeptoids can provide answers to these 3 axes of dealing with infectious diseases through providing active ingredient in for therapeutics, medical devices or biocide use.
Therapeutics – a real need for new molecules
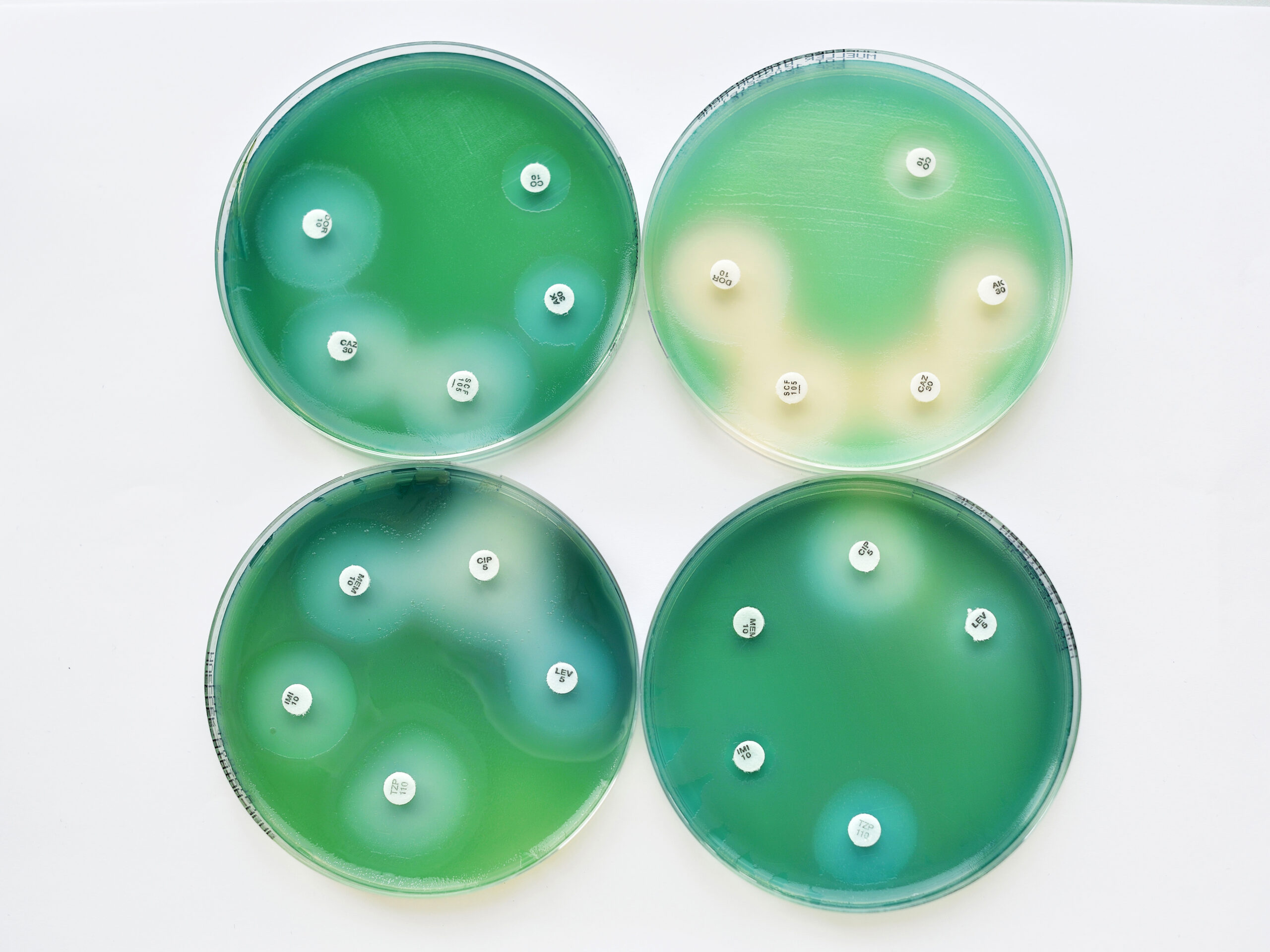
One of the major concerns in the fight against AMR is the insufficient development of new antimicrobial drugs. Pharmaceutical companies face challenges in creating innovative molecules, mainly because of the high costs, lengthy development timelines, and a lack of financial incentives. In recent years, the number of new molecules entering the market has been limited, exacerbating the AMR problem.
In the last decades, only a few new molecules entered in the market creating a snowballl effect on the microbial resistance mechanism. Using the same molecules years after years in the community to treat patient has increased the rize of resistance in microorganisms leading to a decrease of efficacy of the drug being used to treat patients. This is an explanation of the ground breaking projection for 2050 that predicts 10 millions deaths per year due to infections.

Medical devices – a preventive tool
With antimicrobial resistance (AMR) posing a growing threat to public health, the medical devices sector has a crucial role to play in addressing this global crisis
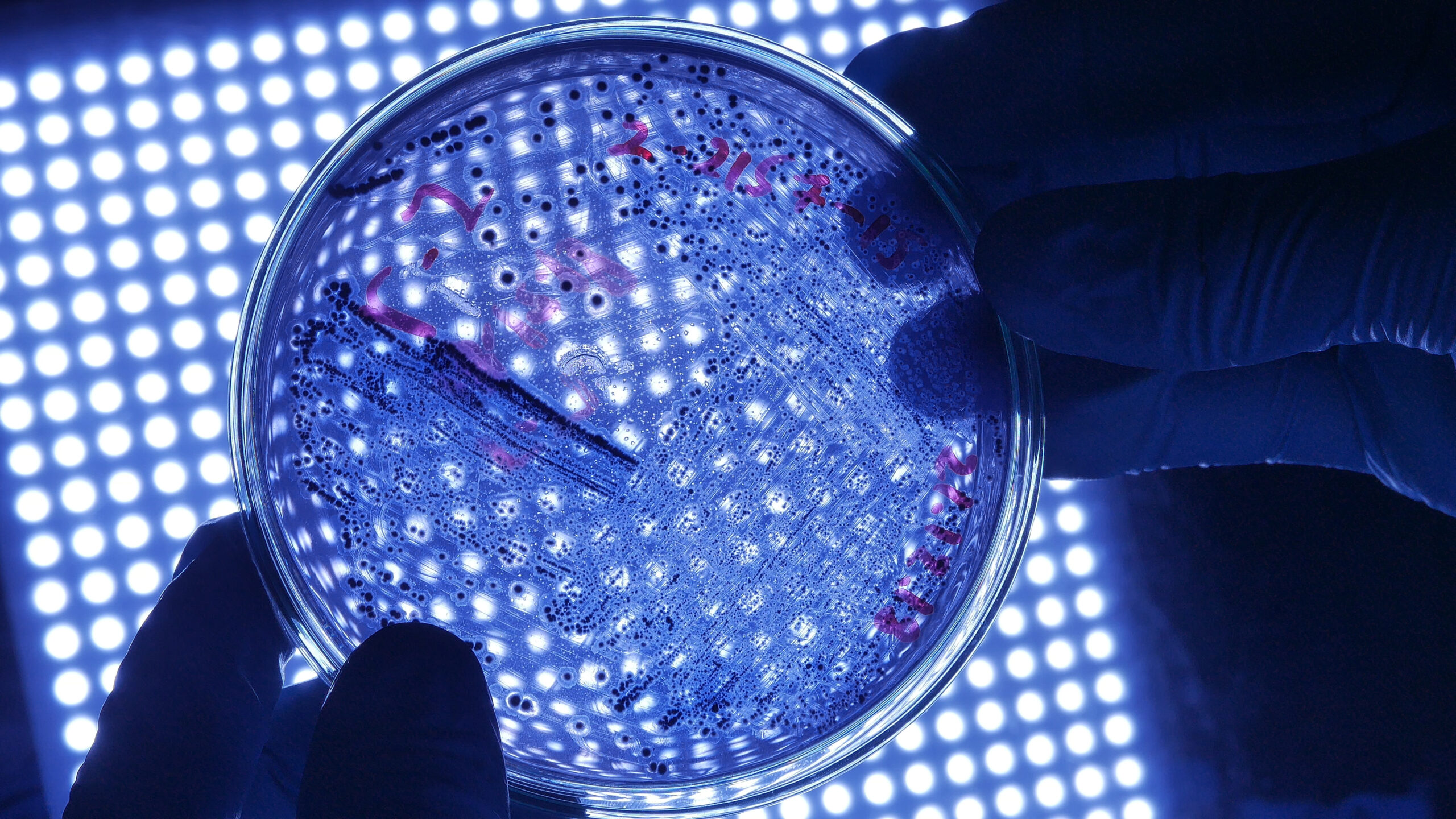
Data indicates that healthcare-associated infections (HAIs) contribute significantly to AMR. According to the World Health Organization, HAIs affect millions of patients annually. Medical devices such as antimicrobial-coated catheters and surgical instruments can help reduce HAIs, minimizing the need for antibiotics. Indeed by minimizing the transmission of infections, these devices reduce the need for antibiotics in the first place.
Biofilm formation is a natural defense mechanism for bacteria and other microorganisms, enabling them to survive in hostile environments, including the presence of antibiotics. Biofilm-related infections on medical devices can lead to repeated or extended antibiotic exposure for patients. The presence of these biofilms poses design challenges for manufacturers. Developing devices that resist or prevent biofilm formation is crucial.
Biocide – an integrated controle solution
Biocide solutions, which include disinfectants, antiseptics, and sanitizers, have the potential to curb the spread of AMR in several ways. Biocide are essential in healthcare settings to ensure surfaces and equipment are thoroughly disinfected, reducing the transmission of AMR-associated pathogens. These solutions can also be crucial for food safety and agriculture or alternatively water treatment.
The sector of biocide solutions plays a vital role in the fight against AMR. By preventing infections, maintaining hygiene, and controlling the spread of pathogens, biocide solutions can reduce the demand for antibiotics and limit the development of AMR. Collaborative efforts between healthcare, agriculture, and public health sectors are essential to maximize the impact of biocide solutions in mitigating AMR.